Introduction: Why AFUE Ratings Matter
When it comes to choosing a furnace, efficiency isn’t just a buzzword—it’s a real factor that affects your energy bills, comfort, and carbon footprint. One of the most reliable ways to measure furnace efficiency is through AFUE ratings, short for Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency. Whether you’re comparing an AFUE gas furnace or exploring other fuel options, understanding this rating system helps you make a smarter investment for your home.
What Is an AFUE Rating?
So, what is an AFUE rating exactly? It’s the percentage of fuel a furnace converts into usable heat during a typical heating season. For example, a furnace with an AFUE rating of 90% means that 90% of the fuel becomes heat for your home, while the remaining 10% is lost through exhaust.
In simple terms:
- A higher AFUE rating = more efficiency, lower bills.
- A lower AFUE rating = wasted fuel, higher costs.
How Furnace Efficiency Is Measured
Furnace efficiency is measured by comparing heat output to fuel input. The Department of Energy requires that all furnaces display their AFUE rating, making it easier for homeowners to evaluate options.
For example:
- High-efficiency furnaces (90%–98% AFUE): These models capture more heat from the combustion process, often using condensing technology.
- Standard efficiency furnaces (80% AFUE): Still common in older homes, but less cost-effective in the long run.
This measurement helps homeowners estimate potential savings before committing to a purchase.
For More Information about the service: How Often Should I Get My Furnace Serviced?
Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency Explained
Annual Fuel Utilization Efficiency (AFUE) is not just a technical label—it’s a standardized calculation regulated across the U.S. and Canada. AFUE takes into account:
- Seasonal fuel use, not just one day of operation.
- Average performance under normal residential conditions.
- Heat lost through the venting system.
That means AFUE provides a realistic picture of how your furnace will perform, not just in perfect lab settings, but in everyday living conditions.
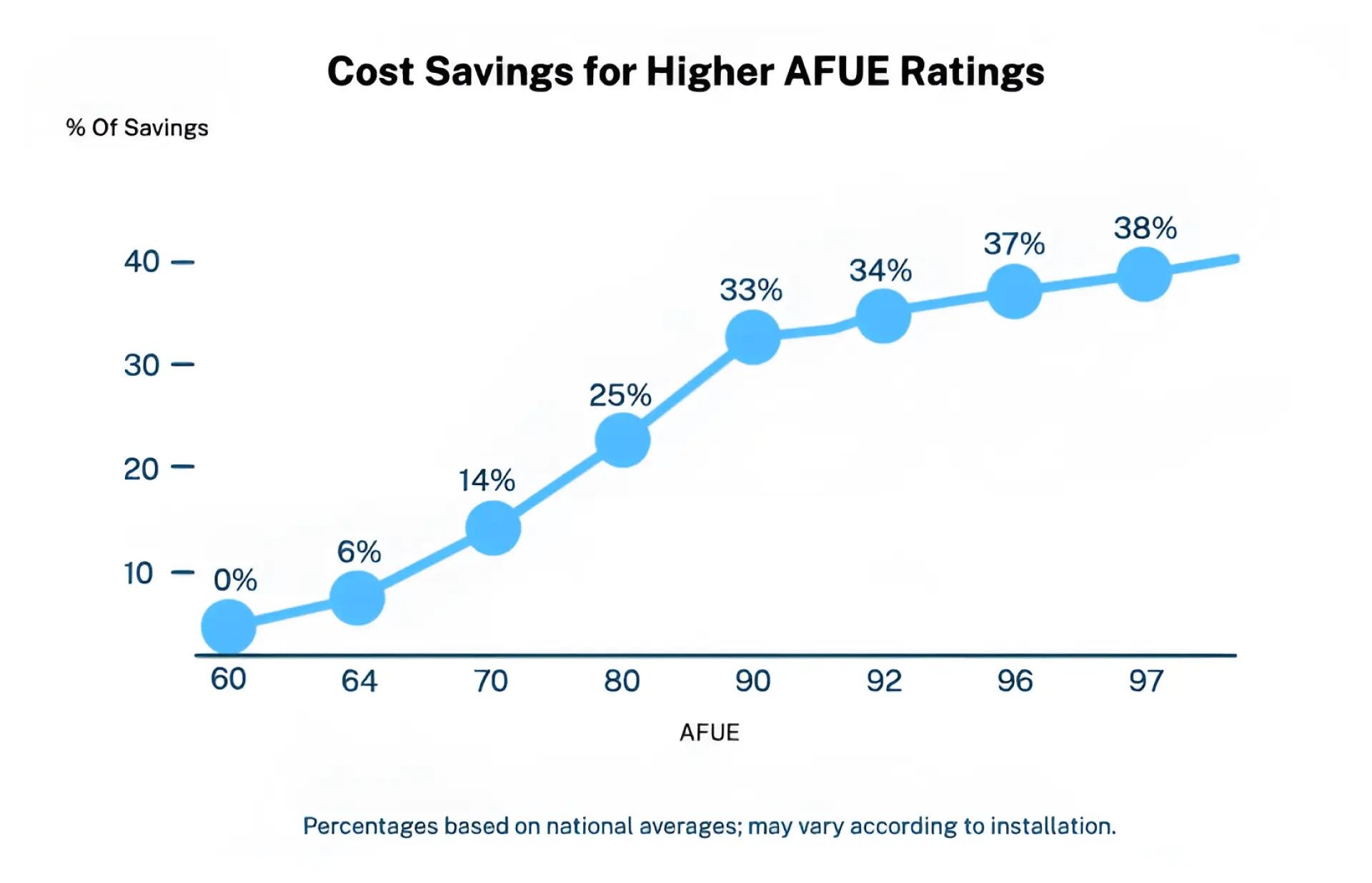
AFUE Rating Chart: What the Numbers Mean
An AFUE rating chart helps visualize the efficiency range:
- 55%–70% AFUE: Older, outdated models; common in furnaces 20+ years old.
- 80% AFUE: Minimum efficiency required for modern furnaces in many regions.
- 90%–98% AFUE: High-efficiency furnaces, often Energy Star certified.
Example: Upgrading from a 65% AFUE furnace to a 95% AFUE gas furnace could cut fuel usage nearly in half—translating into significant savings year after year.
Factors That Impact AFUE Efficiency
Several factors influence a furnace’s efficiency rating:
- Fuel type: AFUE gas furnaces generally deliver higher efficiency than oil or propane systems.
- Age of equipment: Furnaces older than 15–20 years usually score much lower on AFUE efficiency.
- System design: Two-stage burners, variable-speed blowers, and sealed combustion systems can dramatically increase efficiency.
- Sizing and installation: A correctly sized furnace will operate closer to its rated AFUE, while oversized systems waste energy.
For More Information: Why you should clean your furnace!
Comparing AFUE Ratings Across Furnace Types
When comparing furnace AFUE ratings, keep these points in mind:
- Gas furnaces: Widely used, cost-effective, and capable of achieving 95%+ AFUE.
- Oil furnaces: Typically less efficient, often ranging between 80–90% AFUE.
- Electric furnaces: Technically 100% AFUE because no fuel is wasted—but higher electricity costs often make them less economical.
This comparison shows why gas furnaces are the most popular option for households aiming to balance efficiency and affordability.
For More Information: How Long Does a Furnace Last?
Why High AFUE Ratings Matter for Homeowners
A furnace with a higher AFUE rating offers:
- Lower utility bills: Less wasted energy equals real monthly savings.
- Increased comfort: Consistent heating without wide temperature swings.
- Environmental benefits: Reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint.
- Better resale value: Energy-efficient systems are attractive to homebuyers.
Read More Information: How to keep your furnace running in winter!
How to Choose the Right AFUE Gas Furnace
Before you purchase, consider:
- Climate: Colder regions benefit most from furnaces with 95%+ AFUE.
- Budget: High-efficiency models cost more upfront but pay off long-term.
- Fuel availability: Natural gas availability can determine whether a gas furnace is the most practical choice.
- Home insulation: Even the highest AFUE won’t save much if your home leaks heat.
Always compare AFUE ratings side by side when evaluating models, and don’t forget to factor in professional installation quality.
Conclusion: Making Sense of AFUE Ratings
To recap, AFUE ratings are the gold standard for measuring furnace efficiency. They tell you how effectively your furnace converts fuel into heat, using the annual fuel utilization efficiency formula. By studying an AFUE rating chart and comparing options—especially if you’re looking at an AFUE gas furnace—you can choose a system that balances performance, savings, and comfort.
Understanding how furnace efficiency is measured by AFUE empowers homeowners to make informed, cost-effective decisions. If your current furnace has a low AFUE rating, upgrading to a higher-efficiency model isn’t just an energy choice—it’s a financial and environmental win.